★ You can Try To Find More Practice Materials Online~~~ For Example: Flexbox Froggy
Layout
- The fixed width: the width always is 960/ 1000 / 1024 px
- Not Fixed Width: mainly depends on normal flow layout
- The Normal Flow is automatically fitted, no more extra style
- Responsive Layout
- Which means the width fix in the PC, but not fix in the mobile phone
- In other words, mixed layout
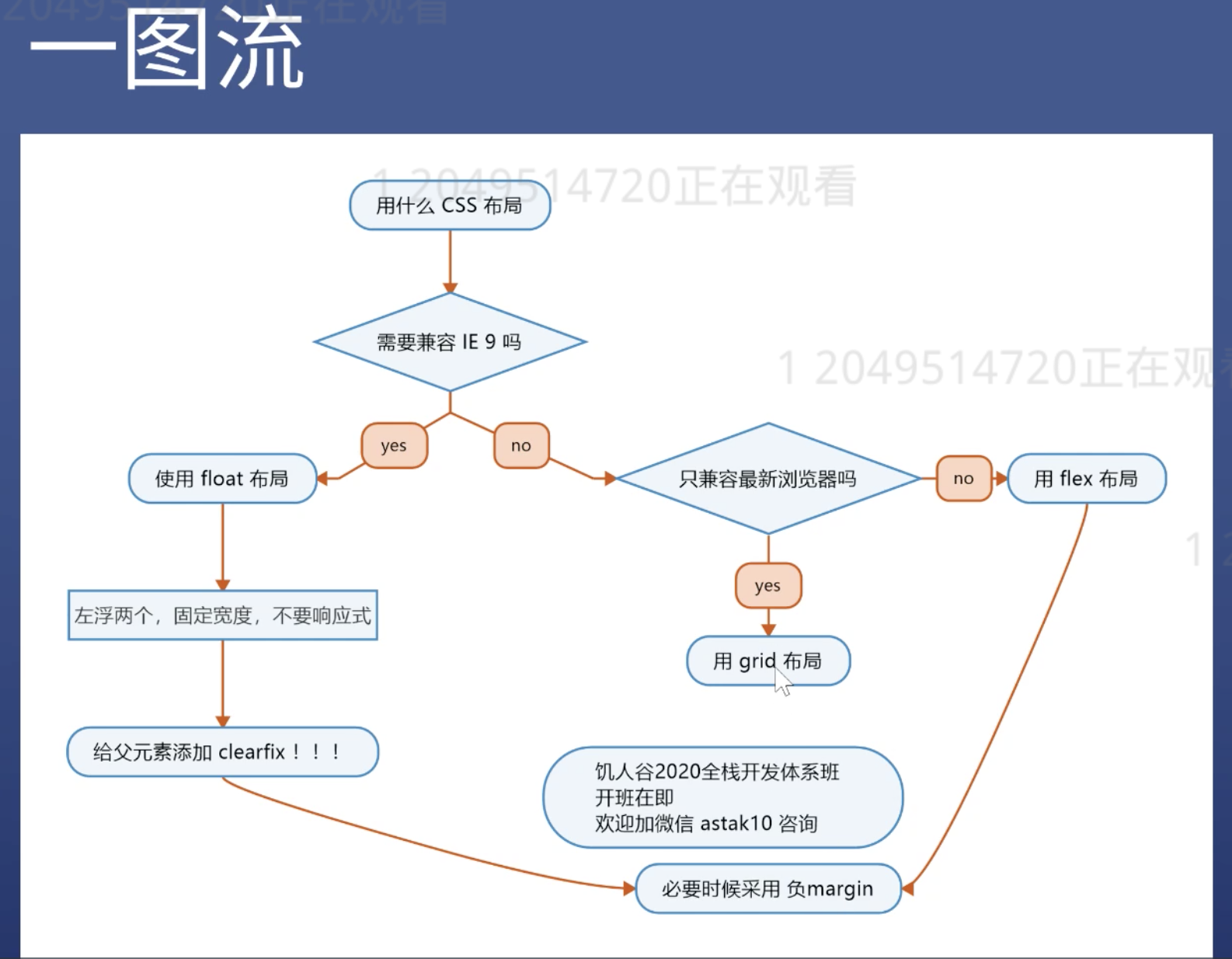
Float
- Add float:left and width in the children elements
- Add .clearfix in the parent element
Important To Remember - Flex
- display:flex;
- flex-direction:row/column
- flex-wrap: wrap
- just-content:center / space-between
- align-items:center
- (These are basic use in work environment)
Regular sketch tools
Grid
- Shortcut to create multiple classes
.a+.b+.c+.d -> press tab
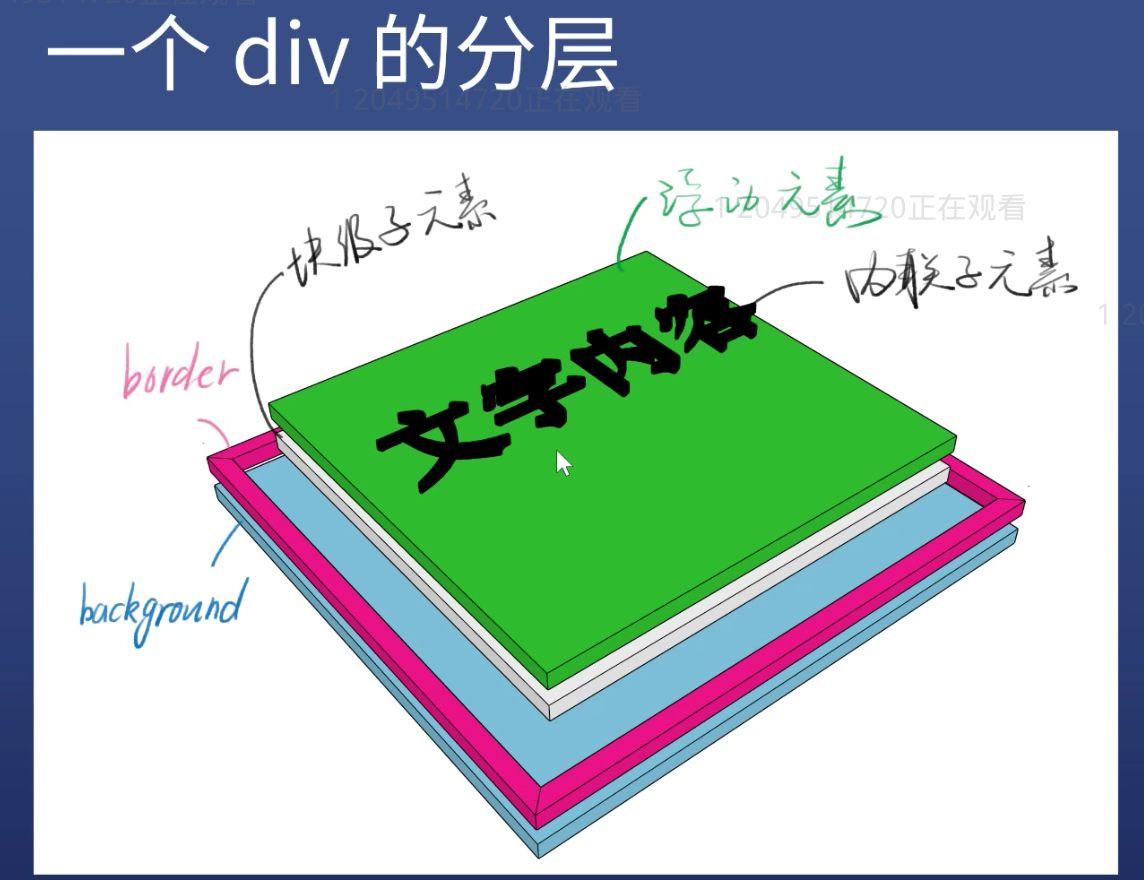
One picture shows the div layout
z-index
The z-index CSS property of a positioned element and its descendants or flex items. Overlapping elements with a larger z-index cover those with a smaller one.
For a positioned box(that is, one with any position other than static), the z-index property specifies:
- The stack level of the box in the current stacking context.
- z-index in the current stacking context level has no interaction with other stack level.
- z-index in the same stack level can be compared.
- Stacking Content Reference
Shortcut to call ‘Console’
- In any tab, press ESC
The Process of the Browser Rendering
Step:
- According to the HTML to construct the HTML Tree(DOM)
- According to the CSS construct the CSS Tree
- Merge two trees into one Rendering Tree
- Layout (Normal Flow, Box Model, Calculate Size and Position)
- Painting (Draw out the border color, font color, shadow)
- Finally compose all the parts together
Rendering Performance (Cramming)
- Optimizing Javascript Execution
- Avoid setTimeout or setInterval for visual updates; always use requestAnimationFrame instead.
- Move long-running Javascript off the main thread to Web Workers.
- Use micro-tasks to make DOM changes over several frames.
- Use Chrome DevTools’ Timeline and Javascript Profiler to assess the impact of Javascript.
- Reduce the Scope and Complexity of Style Calculations
- Reduce the complexity of your selectors; use a class-centric methodology like BEM.
- Reduce the number of elements on which style calculation must be calculated.
- Avoid Large, Complex Layouts and Layout Thrashing
- Similarly to style calculations, the immediate concerns for layout cost are:
- The number of elements that require layout.
- The complexity of those layouts.
- Layout is normally scoped to the whole document.
- The number of DOM elements will affect performance; you should avoid triggering layout wherever possible.
- Assess layout model performance; new Flexbox is typically faster than older Flexbox or float-based layout models.
- Avoid forced synchronous layouts and layout thrashing; read style values then make style changes.
- Similarly to style calculations, the immediate concerns for layout cost are:
- Simplify Paint Complexity and Reduce Paint Areas
- Changing any property apart from transforms or opacity always triggers paint.
- Paint is often the most expensive part of the pixel pipeline; avoid it where you can.
- Reduce paint areas through layer promotion and orchestration of animations.
- Use the Chrome DevTools paint profiler to assess paint complexity and cost; reduce where you can.
- Stick to Compositor-Only Properties and Manage Layer Count
- Stick to transform and opacity changes for your animations.
- Promote moving elements with will-change or translateZ.
- Avoid overusing promotion rules; layers require memory and management.
- Debounce Your Input Handlers
- Avoid long-running input handlers; they can block scrolling.
- Do not make style changes in input handlers.
- Debounce your handlers; store event values and deal with style changes in the next requestAnimationFrame callback.
How to Debug the [Hover] Effect
- Open DevTools
- In the Style Tab, find out [:hov] in the top right conner and click it
- Check [:hover]
- Find out
#demo:hover{transform: translateX(50px)} - Press UP or DOWN key to see the demo box moving 1px each time consecutively
- Press Shift + UP or DOWN , the demo box will move 10px each time consecutively
How to Use Transform to Center the Box (Cramming)
.wrapper1
{
border: 5px solid black;
position: relative;
height: 600px;
}
#demo1
{
width:200px;
height:200px;
border:1px solid green;
position: absolute;
left:50%;
top:50%;
transform: translateX(-50% -50%);
}
Transition
- Not all the properties can use transition
- Display:none => block can not be transited
- Should use visibility:hidden => visible instead
- Background and Opacity can use transition
Animation - KeyFrame Syntax
Animation:
time ||
timing-function = linear ||
single-animation-iteration-count = infinite||
single-animation-direction = normal, reverse...||
single-animation-fill-mode = none, forwards, backwards ||
single-animation-play-state = running, paused ||
keyframes-name