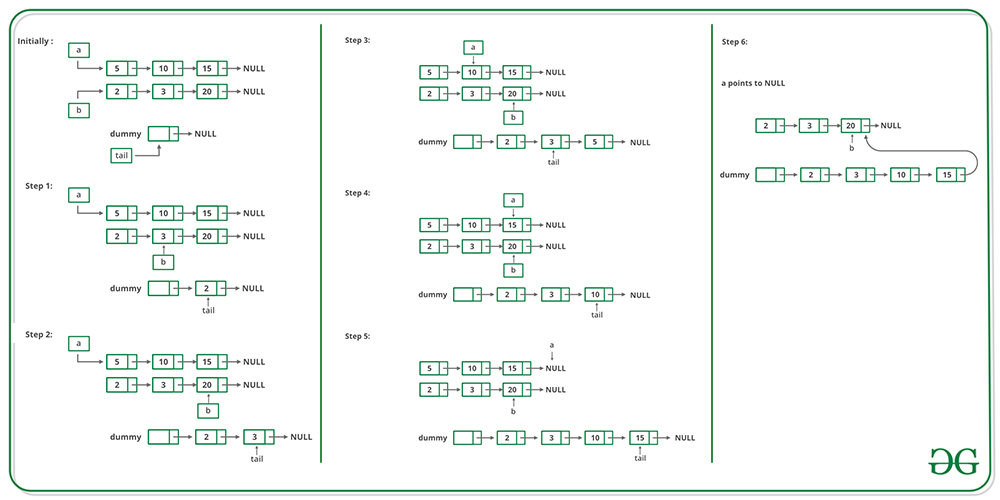
Description
You are given the heads of two sorted linked lists 'list1' and 'list2'.
Merge the two lists in a one sorted list. The list should be made by splicing together the nodes
of the first two lists.
Return the head of the merged linked list.
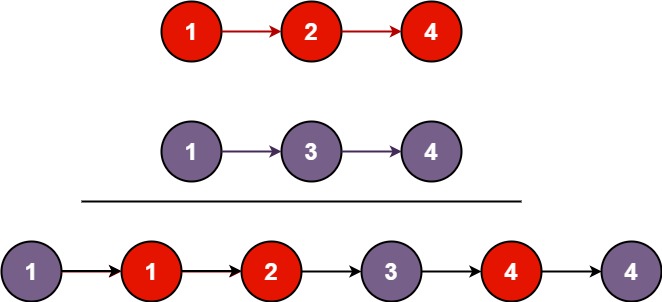
Example 1:
Input: list1 = [1,2,4], list2 = [1,3,4]
Output: [1,1,2,3,4,4]
Example 2:
Input: list1 = [], list2 = []
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: list1 = [], list2 = [0]
Output: [0]
Constraints:
The number of nodes in both lists is in the range [0, 50].
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
Both list1 and list2 are sorted in non-decreasing order.
Thinking
Solution 1 (Without the recursion)
// Definition for singly-linked list.
function ListNode(val, next) {
this.val = (val === undefined ? 0 : val)
this.next = (next === undefined ? null : next)
}
/**
* @param {ListNode} list1
* @param {ListNode} list2
* @return {ListNode}
*/
const mergeTwoLists = (l1, l2) => {
// initialize a LinkedList node with a dummy Node as the head
let dummyNode = new ListNode(-1)
// manitain a reference to the dummyNode head
let head = dummyNode
// while both of passed nodes l1 and l2 has value
while (l1 !== null && l2 !== null) {
if (l1.val <= l2.val) {
// if l1 is smaller, point the dummyNode to the l1
dummyNode.next = l1
// get the next value of l1 list
l1 = l1.next
} else {
// if l2 is smaller, point the dummyNode to the l2
dummyNode.next = l2
// get the next value of l2 list
l2 = l2.next
}
// move into the next level of the linkedlist for the next iteration
dummyNode = dummyNode.next
}
// if l1 has run out of elements
if(l1 === null){
dummyNode.next = l2
}
// if l2 has run out of elements
if(l2 === null){
dummyNode.next = l1
}
return head.next
}
Solution 2 (With the recursion)
// Definition for singly-linked list.
function ListNode(val, next) {
this.val = (val === undefined ? 0 : val)
this.next = (next === undefined ? null : next)
}
/**
* @param {ListNode} list1
* @param {ListNode} list2
* @return {ListNode}
*/
const mergeTwoLists = (l1, l2)=>{
// if either list is empty return the other one
if(l1 === null) return l2
if(l2=== null) return l1
if(l1.val <= l2.val){
l1.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2)
return l1
}else{
l2.next = mergeTwoLists(l1,l2.next)
}
}
Running Time
- This algorithm runs in O(n+m) time, where n and m are the lengths of respective linked lists. This is the running time because to merge both linked lists into one, we need to iterate through each node in the list
dDetailed explanation with graph